Whenever you find your computer is running slow or the Internet seems to be getting sluggish, open the Windows Task Manager. This utility gives you insight into which processes are using the most resources, including the CPU, memory and network bandwidth.
Users often define background processes as any app that is running behind an active window, like a Web browser you forgot to close before opening Excel. In Task Manager, active and background apps are both listed as apps. Background processes are any processes that run behind those apps that don't provide a user interface for you to access.
Video of the Day
Video of the Day
Step 1
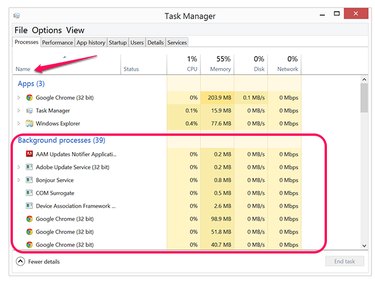
Launch Task Manager by pressing Ctrl-Alt-Delete, or by pressing Win-X and clicking Task Manager.
Click the Name header under the Processes tab. Active apps are listed at the top of the list, Background Processes are listed second, and Windows Processes are listed last, each entry in alphabetical order. In this example, Chrome is listed as an App, but there are also several Chrome background processes, some of which won't close when the Chrome app is closed. Other background processes include software update services and network discovery services. Windows Processes also run in the background but are related to the Windows 8.1 operating system.
Step 2
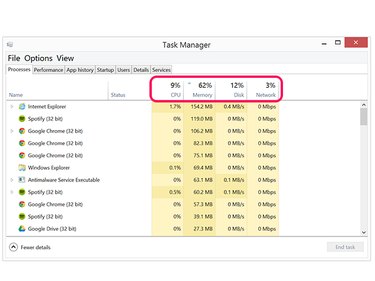
Examine the resources being utilized. Each app or process currently running is displayed on the left, with the resources it is using displayed in the columns on the right. The column headers display the percentage of capacity used by each resource. For example, if the Memory header shows 75 percent, then only 25 percent of your computer's memory is free.
Step 3
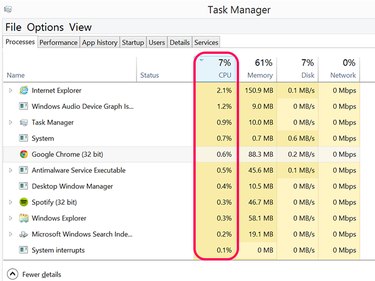
Click a column header to sort that column's processes by the most active.
- CPU is the computer's central processing unit. Games and apps like Photoshop may use a lot of the CPU when they are processing data.
- Memory is the computer's RAM. Any app that uses a lot of CPU power often uses a lot of memory as well. Web browsers can also take up a lot of memory if you've been surfing for a long time, since everything you've seen is usually store in memory until you close the browser tab or window.
- Disk is the hard drive utilization. Any process reading data from the hard drive, or saving data to the hard drive, is displayed here.
- Network shows the amount of data traveling across your network. High definition video streaming and file transfers usually take up the most network bandwidth.
Step 4
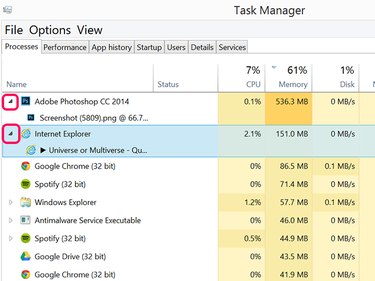
Click the Arrow beside a process to get more information about it. For example, if you have more than one Internet Explorer window open, clicking the Arrow lets you see the name of the active tab.
Step 5
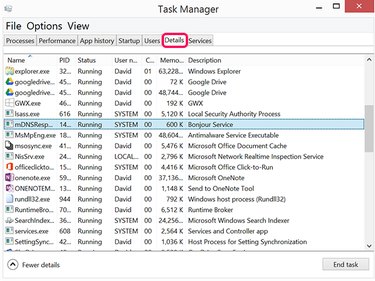
Click the Details tab if you're not certain what a process does and scroll through the listings to find it. The description for each process displayd on the right.
Step 6
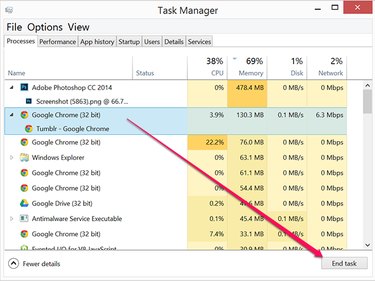
Select the process under the Resources tab or the Details tab that you want to end. Click the End Task button. The process is terminated immediately, and Task Manager should reflect that those resources are now free.
Step 7
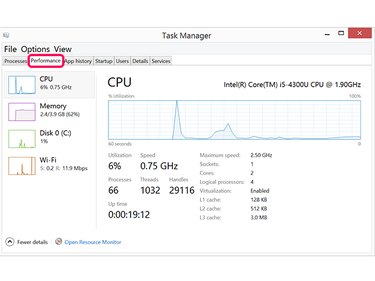
Click the Performance tab to see details of the computer's performance. The graph is updated live so you can watch for spikes in performance. If you closed an app that was using a lot of the CPU resources, for example, leave Task Manager open when you re-launch the app. The graph can show you the effect that the app has on the CPU in real-time.
Step 8
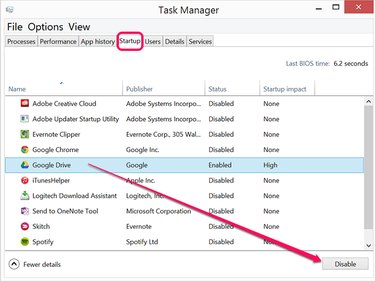
Click the Startup tab to review the processes that launch whenever you turn on your computer. Task Manager displays the impact each app has on your computer's startup time. Select any apps that you don't use often and click the Disable button. This not only reduces your computer's startup time, but increases the amount of resources you have to launch other apps.