
Use the Format command to format a removable storage device, such as an SD card, directly from the Command Prompt in Windows 7 and 8.1. You can include the command in a batch file and format the card by running the file. You can even run the file at startup to automate the task.
Step 1: Connect the Drive and Retrieve the Drive Letter
Connect the SD card to the computer. If your computer doesn't have a built-in SD card reader, use an USB SD card reader. Avoid USB hubs whenever possible, and connect the card reader to a USB port on the computer itself.
Video of the Day
Press Windows-X to display the Power User menu, and then click File Explorer.
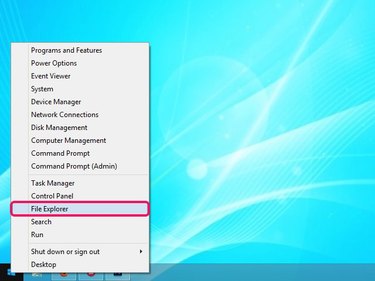
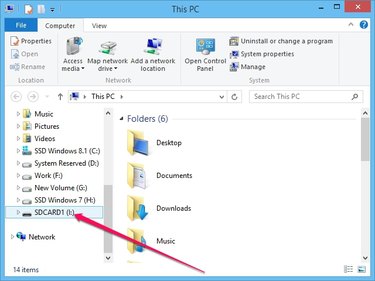
Locate the drive assigned by Windows to your SD card in the left pane and remember or write down the drive letter.
Step 2: Use the Format Command
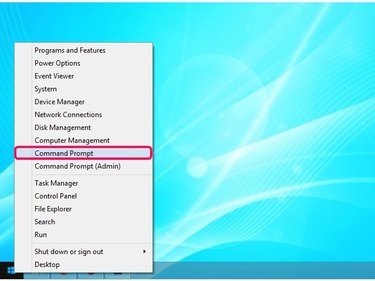
Press Windows-X to display the Power User menu, and click Command Prompt to launch the utility.
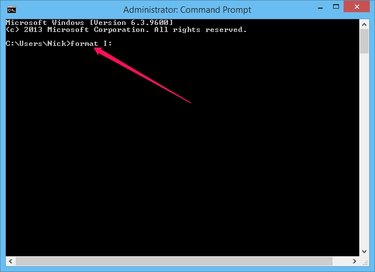
Type format letter: and press Enter to format the drive. Don't forget to replace letter with the correct drive letter, for example format e: for the E drive. Press Y and then Enter to confirm your action if you are sure you want to erase the contents of the SD card. The format command without any parameters formats the drive using the default size and type.
Append the /fs:FORMAT parameter to the command to specify the file system to use. You can replace FORMAT with FAT, FAT32, NTFS or UDF. Example: format I: /fs:FAT32.
Type format letter: /q to perform a quick format -- Windows does not scan for bad sectors with this parameter. Example: format I: /q.
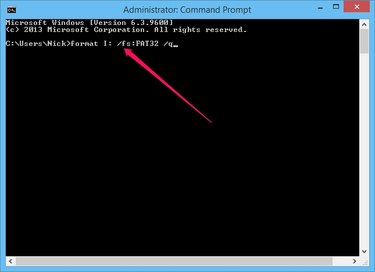
Append the /v:MySDCard parameter to assign a volume label -- the volume label is the name of the drive -- to the drive. Example: format I: /v:MySDCard.
To manually specify the allocation unit size -- the size of individual blocks on your hard drive -- for the file system, append the /a:SIZE parameter. The default size used by Windows is good for standard users. Example: format I: /fs:FAT32 /a:1024.
To dismount the volume before formatting it in order to avoid errors if the volume is in use, append the /x parameter. A dismount forces all open file handles to close so that nothing else can access the data on the card while Windows formats it. Example: format I: /q /x.
Step 3: Test the Result
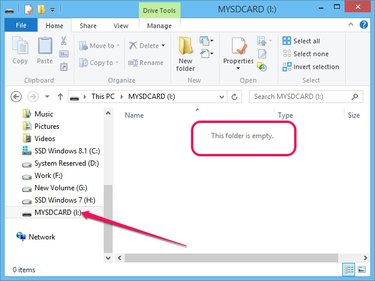
Open File Explorer and select the SD card drive. Ensure it is formatted properly by looking at the right pane. A formatted drive does not contain any files or folders.
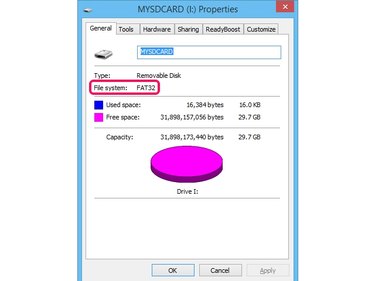
Right-click the drive, select Properties and then ensure the device uses the correct file system -- it is displayed in the File System section of the General tab.
Video of the Day